
If you want to keep the original array, clone the array, then use splice on the cloned array.įrom an SO question about cloning arrays: Note that this modifies your original array. Let leftSide = letters.splice(0, Math.ceil(letters.length /2)) Let leftSide = myArray.splice(0, Math.ceil(myArray.length / 2)) įor example: let letters = Let arraySecondHalf = yourArray.slice(halfwayThrough, yourArray.length) Let arrayFirstHalf = yourArray.slice(0, halfwayThrough) or instead of floor you can use ceil depending on what side gets the extra data Let halfwayThrough = Math.floor(yourArray.length / 2) You can get around this by using slice instead of splice Example let yourArray = props.someArray log the original object and see that its value has been changedĬonsole.log(myObj) // will log Īs you can see the object myObj had the value of key changed as well. change the value of a key in the new const assign a new const to the object (this is assigned by reference)
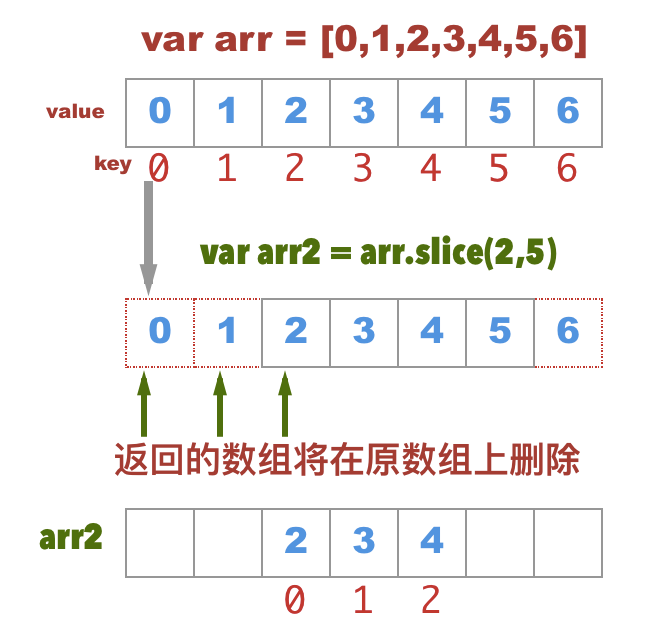
This means that if you use the original reference you will get the new value. When you mutate an object or array you change that original reference. You can always tell if a method will mutate by whether or not it returns a new array or object. Using an array method like splice will cause the original array to be manipulated.

What is a Mutation?Ī mutation is when you change a non primitive, like an object or array. If you need to avoid mutations, for example if you have to split an array in react you don't want to mutate the original or it could lead to some very strange behaviour in your app.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
